Expectations of Sustainable Development
Founded in 1969, Pou Chen Corporation adheres to its core value to go through different stages of development. From initial start-up, quickly growth-up to global expansion, the Company now is one of the leaders in the industry. Meanwhile, the Company has continued to greatly values corporate governance by respecting for shareholder rights, making efforts to increase the structure and capabilities of the Board, including the setup of independent director system, formulating "PCC’s corporate governance best practice principles," "PCC’s ethical corporate management best practice principles", "PCC’s corporate social responsibility best practice principles", etc., to establish corporate governance frameworks so as to exercise corporate social responsibility, in order to further raise the Company’s value and to strengthen its competitiveness.
Today, Pou Chen Corporation has become a total solution provider in footwear supply chain operating on a global basis; it recognizes it has a duty to implement good corporate social responsibility policy that proactively adapts to the ever changing environment so as to enhance social values among its stakeholders.
Pou Chen Corporation sees that corporate social responsibility as an integral part of the business and a necessity to ensure the sustainable development of the Company. Besides, the Company realizes the importance to communicate and cooperate with stakeholders i.e. government, upstream and downstream suppliers, community and employees, etc. so that each feels they are fairly treated and can look forward to the future.
Pou Chen Corporation treats sustainable development as its guideline; it will continue to focus on its core businesses, to treasure talents, to instate manufacturing excellence model, to elevate supply chain efficiency and innovativeness as to pay attention to energy saving, eco-friendly environment, social participation and charity. The Company will endeavor to fulfill its corporate social responsibility initiatives and to promote economic, environmental, and social advancement for purposes of sustainable development.
Corporate Social Responsibility Policy
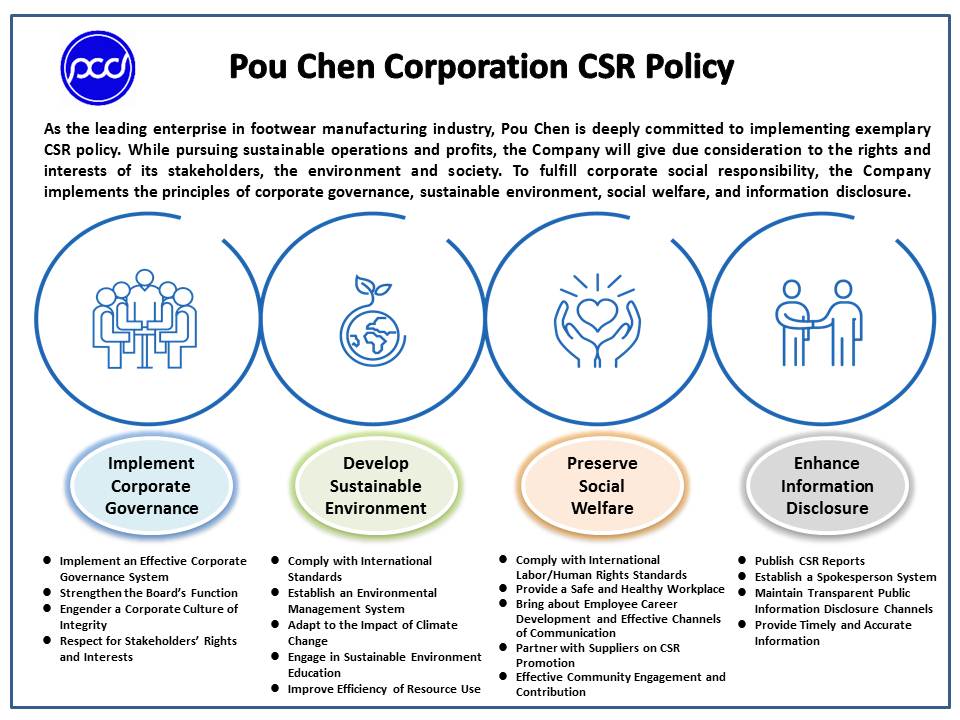
Code of Conduct
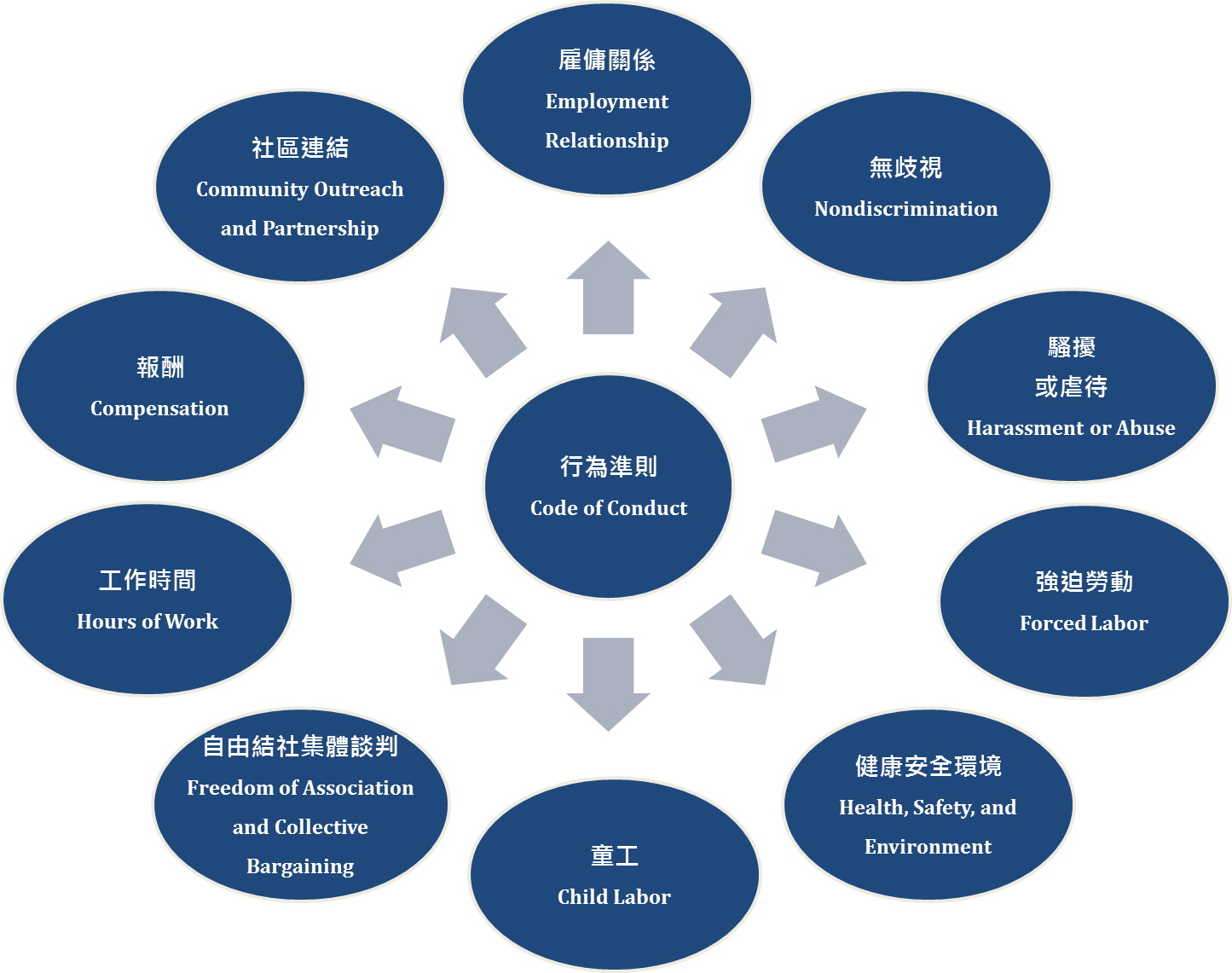
Organizational Structure for CSR Operations
Pou Chen has established the Sustainable Development Department responsible for affairs related to corporate social responsibility. The semi-annual performance meeting is used to examine and review the effectiveness of related CSR measures. Besides, the Sustainable Development Department periodically reports to the Board regarding the planning, progress and effectiveness of CSR as least once a year.
Risk Assessment
| Type | Risk Identification | Risk Control Measures |
| Economy | Market Image Changes | (1) Continuing in facilitation management performance following management principles of professionalism and ethic. (2) Valuing corporate governance, environmental protection, social responsibilities, and implementation of risk control, actively implementing the long-term goal of corporate sustainability. (3) Continuing facilitation in information transparency, and strengthening the interactions and communications between stakeholders to effectively showcase the Company value. |
| Integrity and Anti-Corruption | (1) Stipulating internal regulations such as “Code of Conduct”, “Code of Ethical Conduct”, “Ethical Corporate Management Best Practice Principles”, “Procedures for Ethical Management and Guidelines for Conduct” and “Handling Procedures for Whistleblowing on Illegal and Immortal or Unethical Conducts” to shape a benign governance culture of the Company. (2) Ongoing educational campaigns and training sessions on integrity and anti-corruption. |
|
| Operational Risk | (1) Continuing investing resources in automation, advanced technology and process improvement in response to industry trends and environmental changes for accumulating competitive edge and increasing production efficiency. (2) Utilizing production strengths at each location, maintaining maximal flexibility in capacity allocation, and increasing agility and diversity in operating capabilities. (3) Providing value-added service and introducing innovative production models to deepen the partnership with brand customers. |
|
| Financial Risk | Ongoing focus on financial market changes and economic indicators, selecting appropriate interests rate and exchange rate hedging measures; active management on customer risk, and prudent investment evaluation and management. | |
| Information Risk | Establishing a sound information management, multiple control and protection on internet information security, and strengthening of information security active protection and alert capacities. | |
| Legal Risk | (1) Ongoing inventory and compilation of the latest changes in laws and regulations as well as holding educational campaigns and training sessions, to implement various laws and regulations. (2) Assistance in providing legal consultation and contract review to reduce business controversies. |
|
| Environment | Climate Change Risk | (1) With international climate change risk management trends, relevant impact risks are promptly assessed, and relevant adaptation and prevention measures are stipulated. (2) In cooperation with relevant energy use and emission reduction policies required by the local governments, the Company gradually promotes clean and low-carbon fuel alternatives and seeks energy conservation and carbon reduction opportunities. (3) Through ongoing inventory of energy resource usage and source management, monthly check and analysis on the footwear manufacturing facilities’ energy usage and carbon emission are made, and promotion on energy conservation and carbon reduction action plans are stipulated accordingly. |
| Change in Environmental Protection Laws and Regulations | (1) Inspection on compliance to local laws and regulations in operation bases is reinforced, with regular review on the factories’ conformity to environmental assessment document and rectification plans for non-conformed items. (2) Active investment in pollution prevention facilities and monitoring is taken, and pollutant matters emission compliance management is reinforced. (3) Environmental safety and health internal information management system and incidents reporting system are reinforced to effectively monitor risk events in daily operations. |
|
| Society | Infectious Disease Control Risk | Strengthen disease prevention measures including factories access control measures, incidents handling measures, factories disinfection measures, employee self-health management and health checkup, epidemic reporting mechanism and logistics medical care mechanism, inspection and storage of epidemic prevention materials are reinforced. |
| Fire Safety Management | (1) Continuing implementation of fire prevention measures and strictly fire source control have been taken. (2) Enhancing employee’s fire prevention awareness, fire extinguishment and self-safety inspections. |
|
| Safety and Health Risk | (1) Workplace Safety and Health Committee is established for regular examination on workplace safety concerns and corresponding improvements. (2) Workplace Safety culture is promoted, with ongoing employee occupational safety and health employee training have been taken. (3) Hazardous risk protection measures and operating procedures are reinforced to ensure the safety and production order at workplace. |
|
| Human Resources Risk Management | (1) Continuing conducting risk management and control on affairs including compliance to local laws and regulations, recruitment, performance management, compensation management, training development, labor laws adjustments, and employee management at operation locations. (2) Ongoing optimization on recruitment channels and processes, calibrating on compensation and remuneration market level, and reinforcement to employee care measures. |
|
| Product Quality Management | (1) A strict following on international regulations and branded customer’s MRSL standards for use of raw materials has been taken throughout the product development process from development, trial production to mass production. (2) Relevant product quality policies and measures are comprehensively promoted. (3) “Needle Breakage” protection and“ Metal Detection Measures” are carried out during the manufacturing process to prevent consumers being injured when using the products. |
|
| Product Safety Management | (1) Relevant product safety management regulations are stipulated and education and training are strengthened, including development and design management, material management, production safety management, factory safety management, information system safety management, transportation safety management and trade secret safety management, intellectual property rights maintenance, crises handling, etc. (2) Pursuing sustainable goals of “zero leakage”, “zero accident” and “ zero losses”, the development center and overseas factories continue to implement production safety auditing to solve problems proactively and effectively. |

